בזמני כאשר למדתי שפת תכנות Java, עשיתי ארבה שעורי בית – כלומר כתבתי ארבה קוד ב-Java כמעת כל יום, החלטתי לעבור יחד אתכם בחלק מהקוד שכתבתי עם הסברים שלי ובכך ללמוד שפת Java דרך דוגמאות.
אז ברוכים הבאים ל-Java בעמוד הזה יש צילומי מסך עם הסברים שלי בסרטון וידאו לכל צילום וצילום.
להלן סרטון וידאו עם הסבר לכל צילומי מסך שיש בעמוד הזה:
if(n%2==0){
System.out.println("even number");
}else{
System.out.println("odd number");
}
}
public static void Switch(int n) {
switch (n) {
case 10:
System.out.println("10");
break;
case 20:
System.out.println("20");
break;
case 30:
System.out.println("30");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Other");
}
}
public static void ForFun(int n, int arr[]){
for(int i:arr){
System.out.println(i);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
public static void WhileFun(int n){
while(n<=10){
System.out.println(n);
n++;
}
do{
System.out.println(n);
n++;
}while(n<=10);
}
//Anonymous object class Factorial { void factorial(int n) { int factorial = 1; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { factorial = factorial * i; } System.out.println("factorial is " + factorial); } }
class StaticClass { static int n = 0; public StaticClass() { n++; System.out.println(n); } }
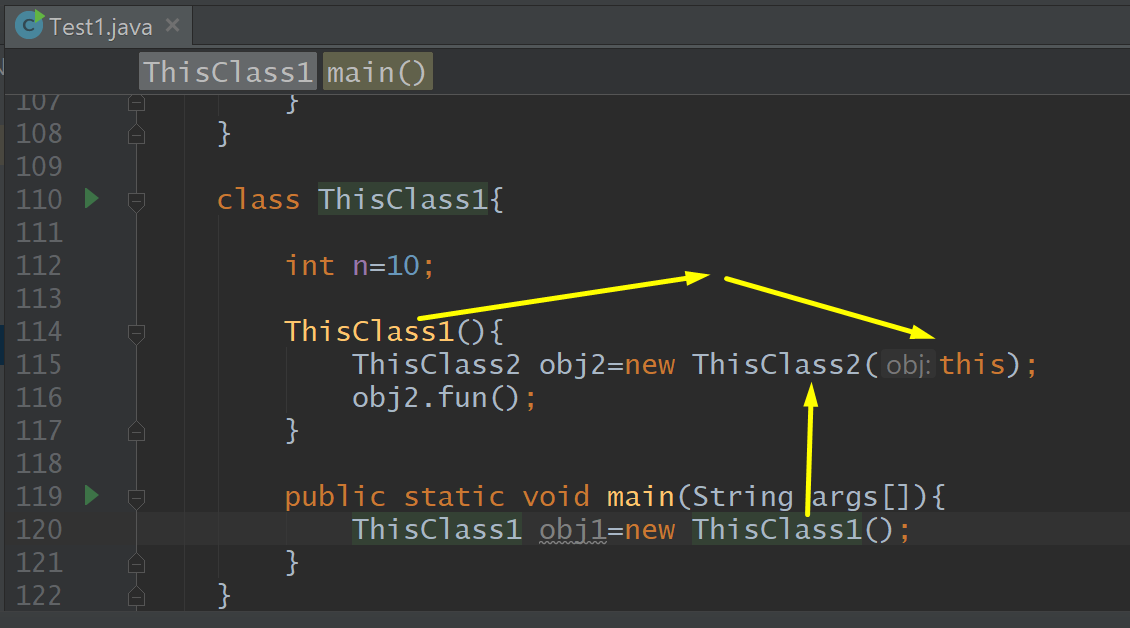
class ThisClass2{ ThisClass1 obj; ThisClass2(ThisClass1 obj){ this.obj=obj; } void fun(){ System.out.println(obj.n);//10 } } class ThisClass1{ int n=10; ThisClass1(){ ThisClass2 obj2=new ThisClass2(this); obj2.fun(); } public static void main(String args[]){ ThisClass1 obj1=new ThisClass1(); } }
class Animal{
void fun(){System.out.println("Animal eats");}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
void fun(){System.out.println("Dog eats");}
}
class Cat extends Dog{
}
class Inheritance{
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog obj1=new Dog();
obj1.fun();//Dog eats
Cat obj2=new Cat();
obj2.fun();//Dog eats
Animal obj3= new Cat();
obj3.fun();//Dog eats
}
}
interface Test2{}
class A implements Test2{
public void a(){System.out.println("A");}
}
class B implements Test2{
public void b(){System.out.println("B");}
}
class Test3{
void fun(Test2 x){//Test2 x=new B();
if(x instanceof A){//False
A a=(A)x;
a.a();
}
if(x instanceof B){//true
B b=(B)x;//B b=new B();
b.b();//B
}
}
}
class Test4{
public static void main(String args[]){
Test2 a=new B();
Test3 b=new Test3();
b.fun(a);
}
}
Interface
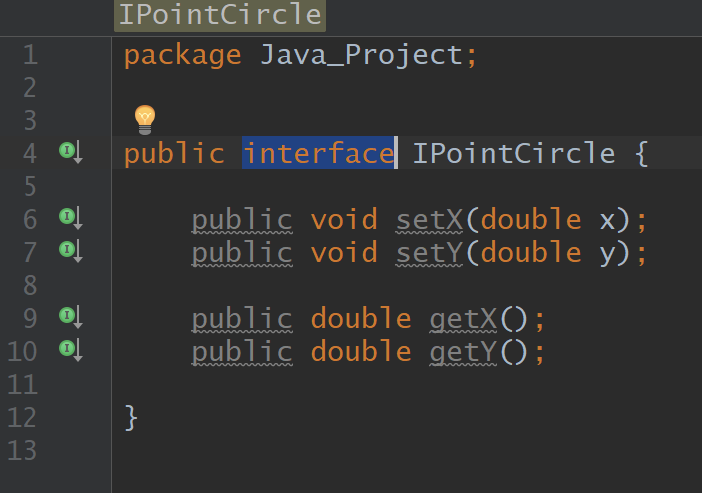
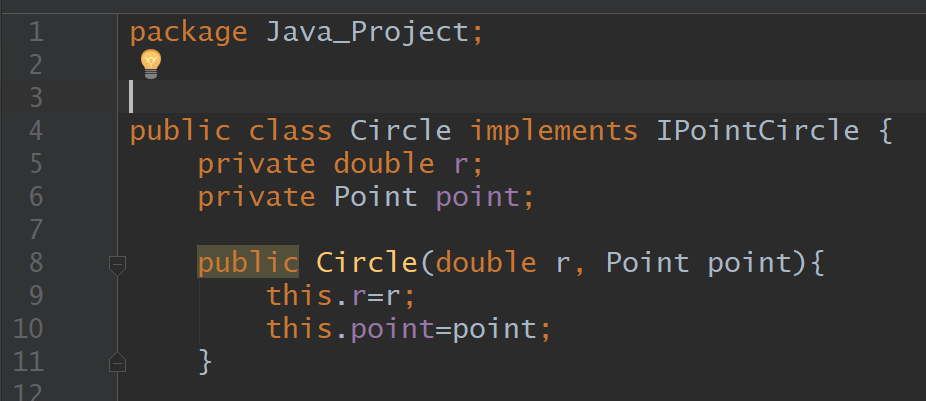
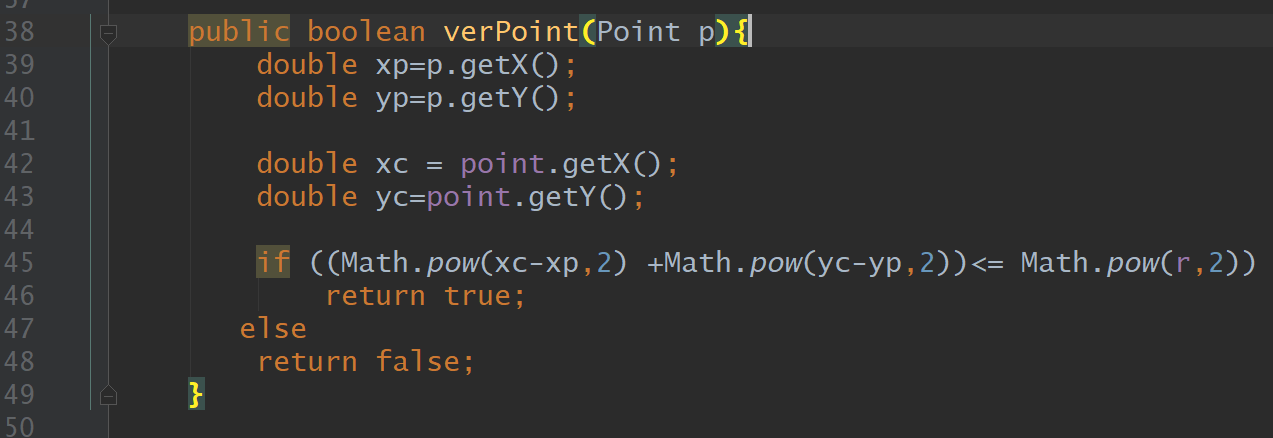
Implements

Get Object by Function
Get Object_array by Function
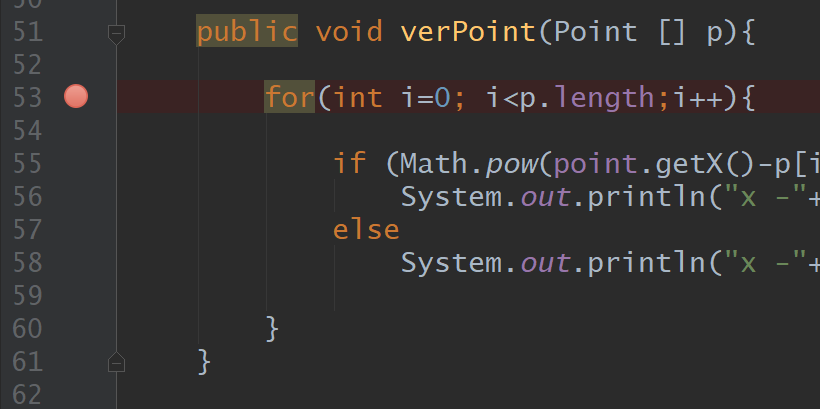
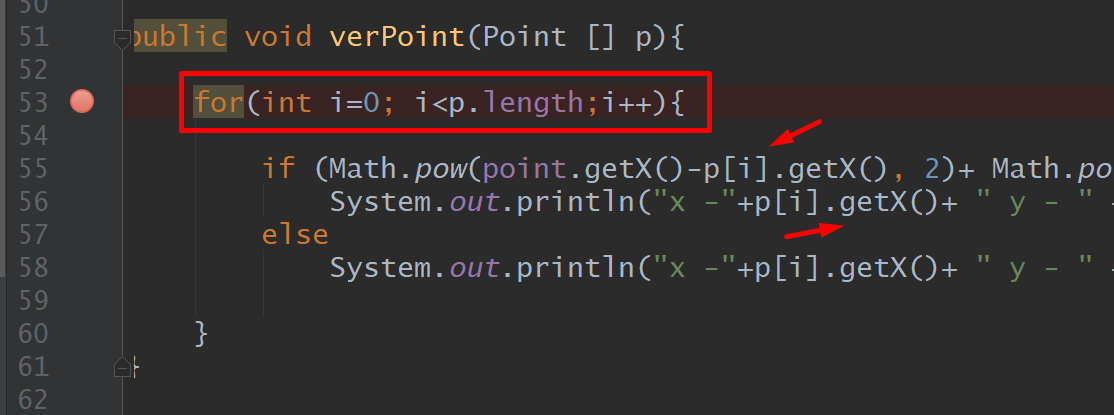
For, Array, Object, If
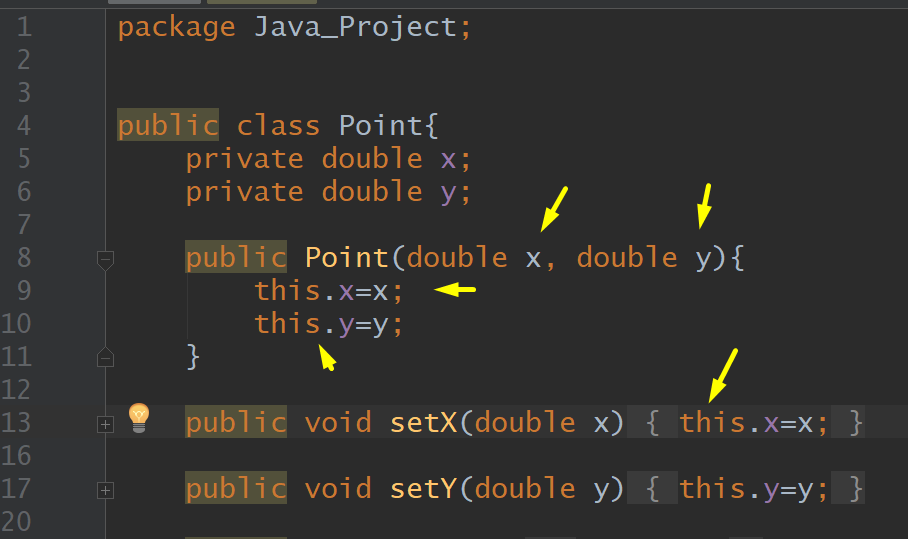
This Object
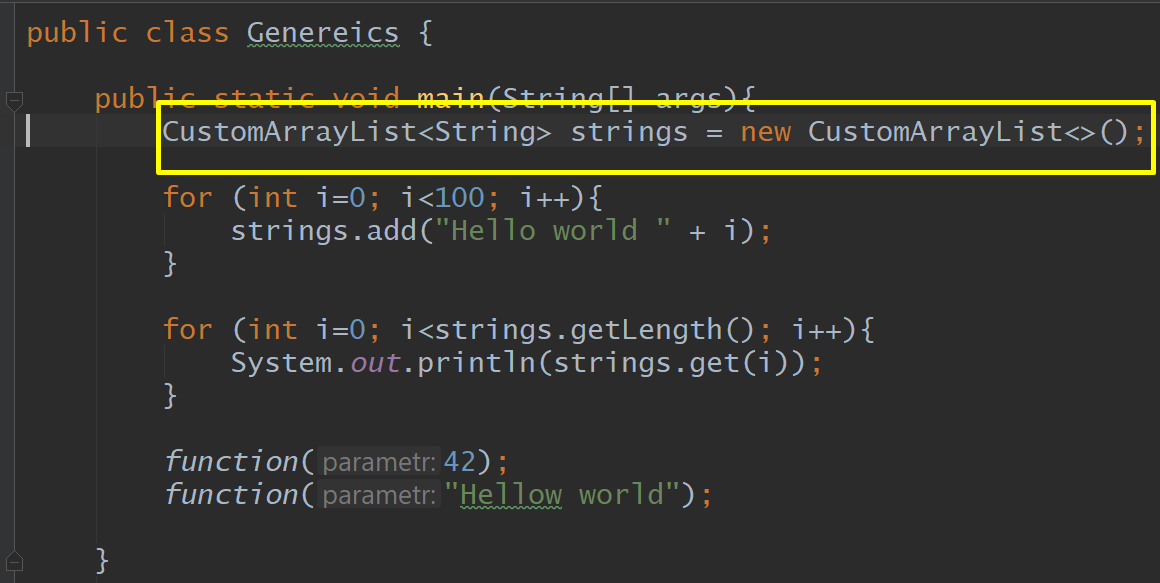
Genereics
<String>
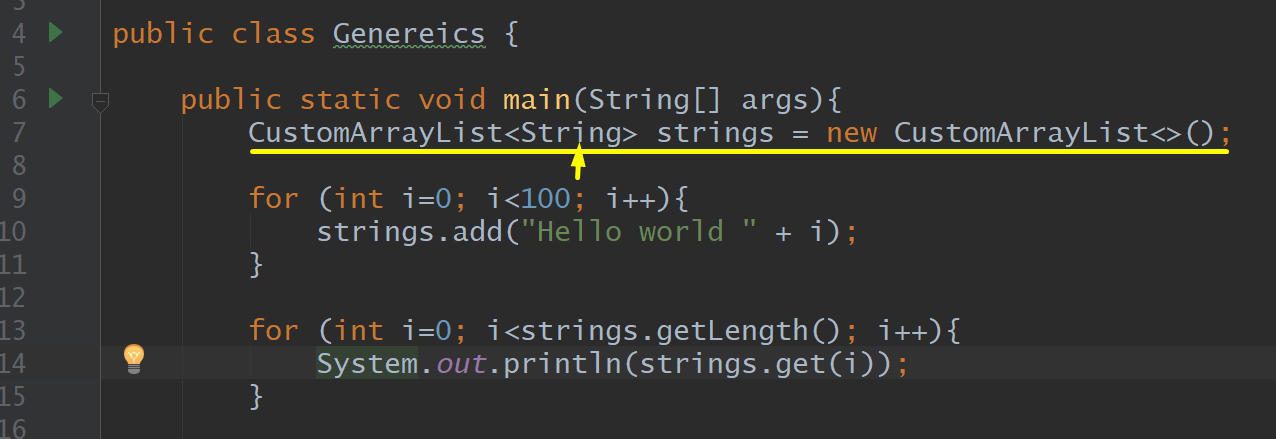
Strings.getLength, Strings.get
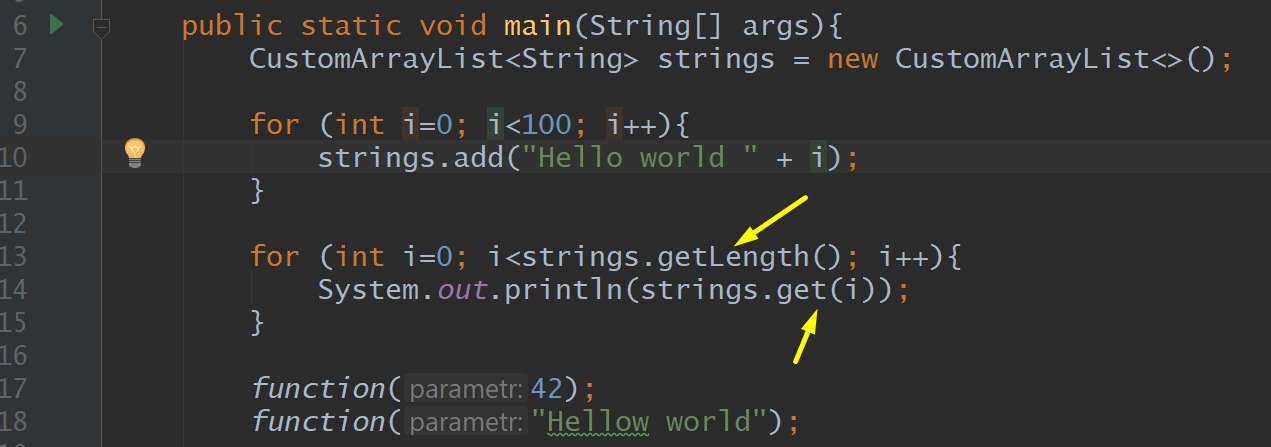
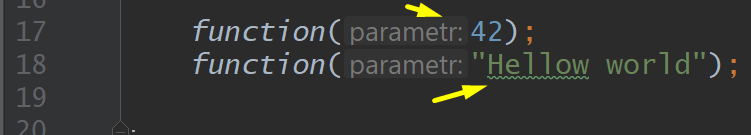
Static, <GENERIC_TYPE>

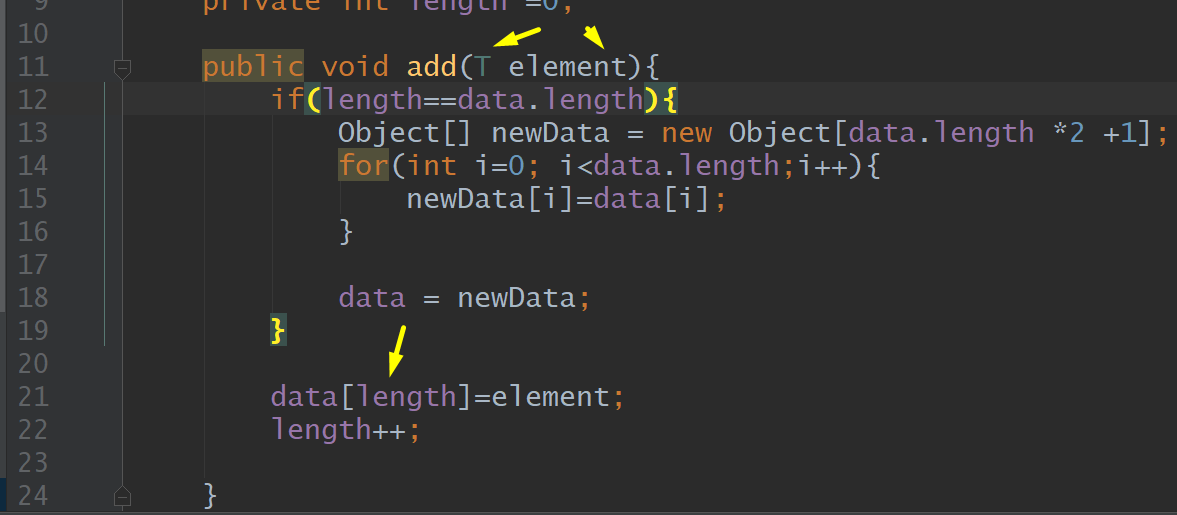
CustomArrayList, Add to Array with T element
Get (T) data[index], Exception
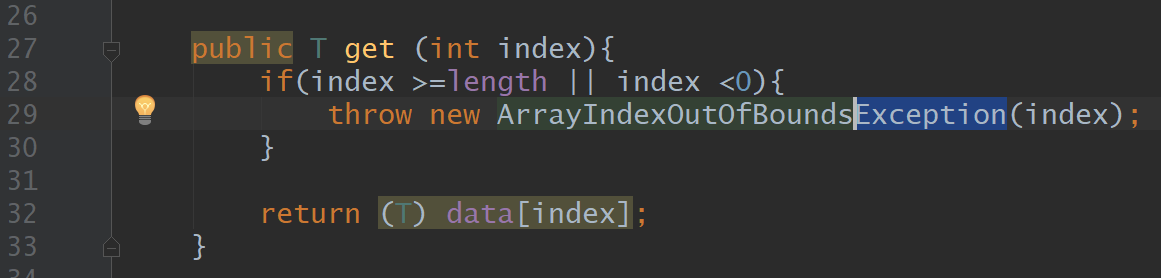
Clear
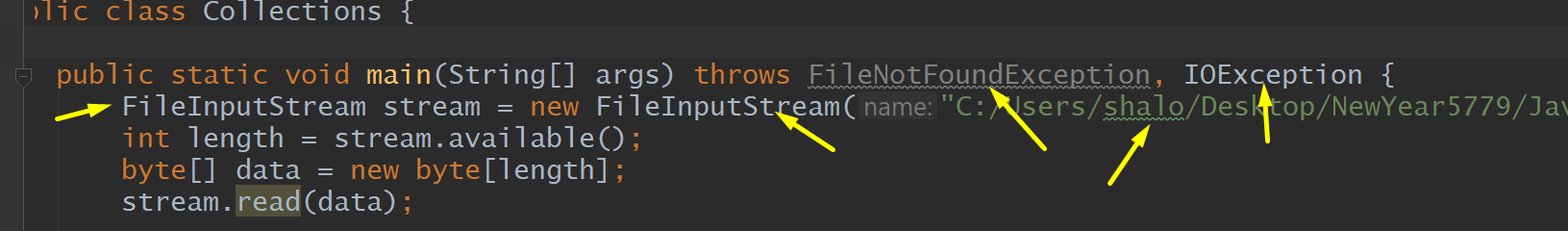
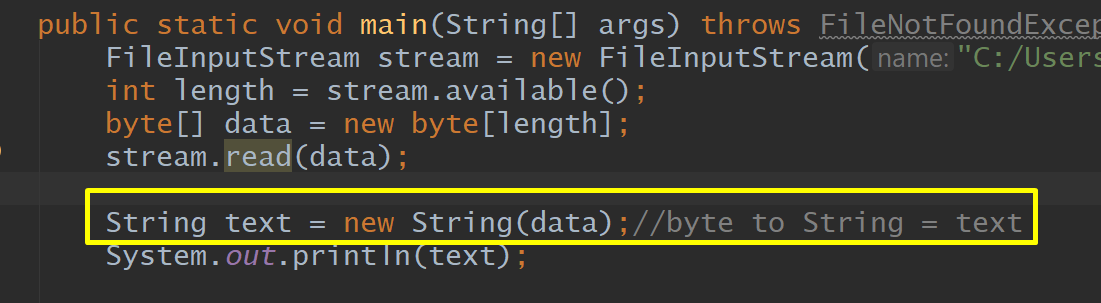
Collections, Exception, FileInputStream, Get File
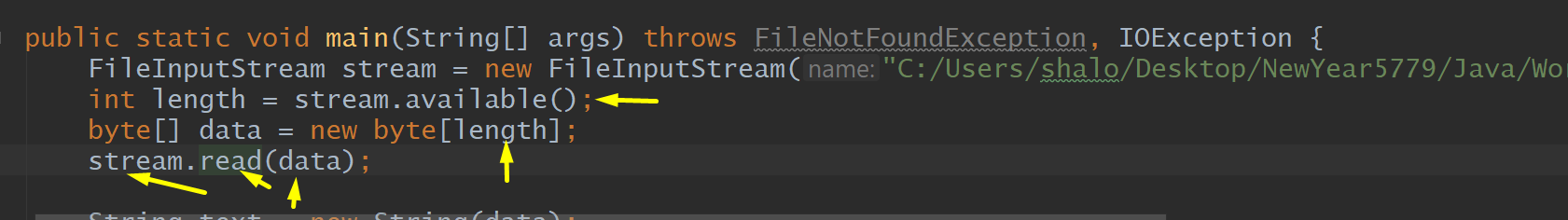
length, Array-Bit, Read file and put it on Data
Byte to String
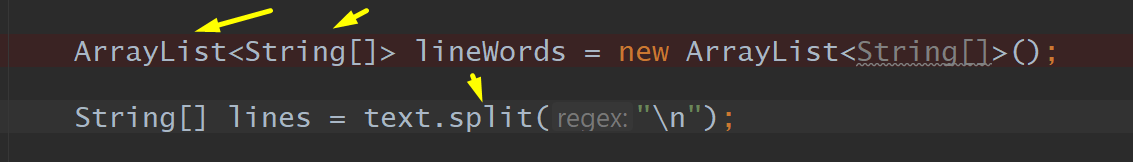
ArrayList, Split, Array [], Straings
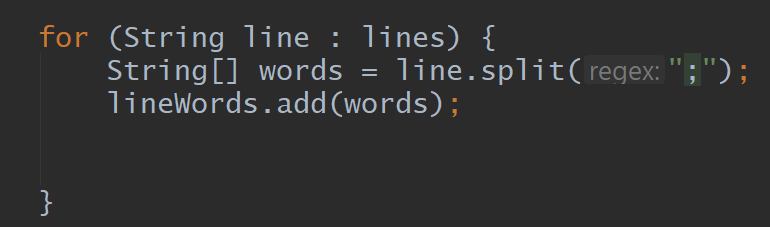
Add, ArrayList, Split, For
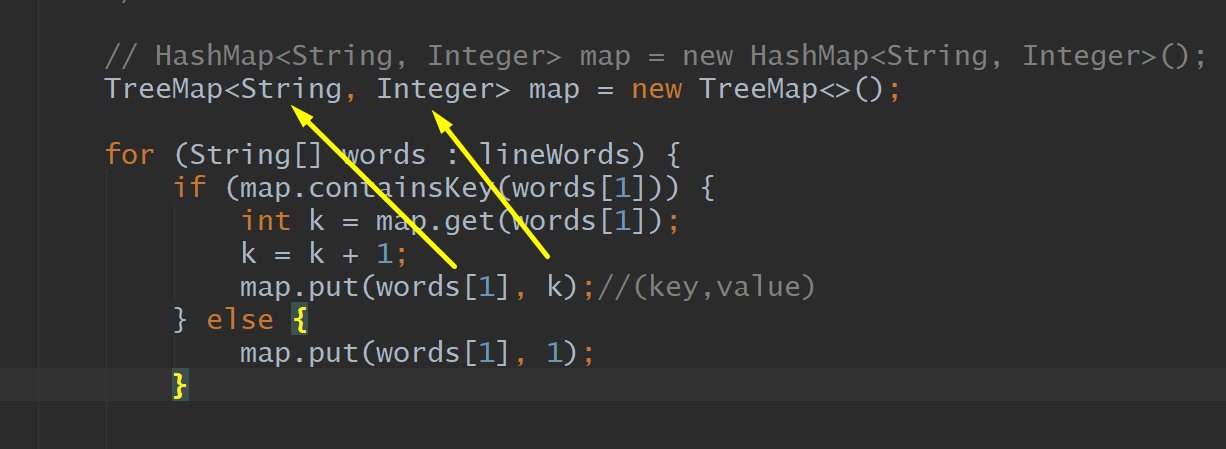
HashMap, TreeMap
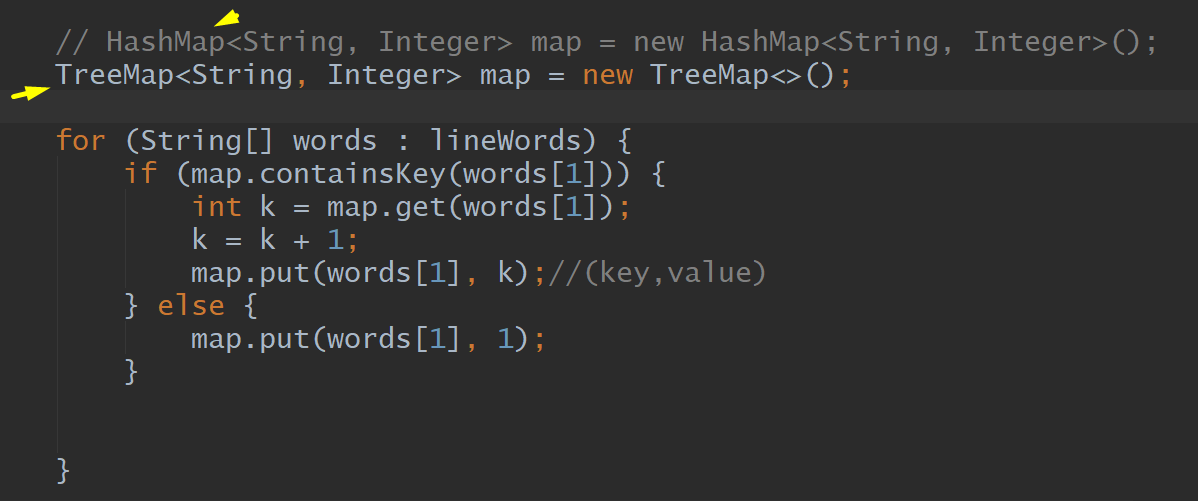
For, String, Array, Map, If, Put, Get
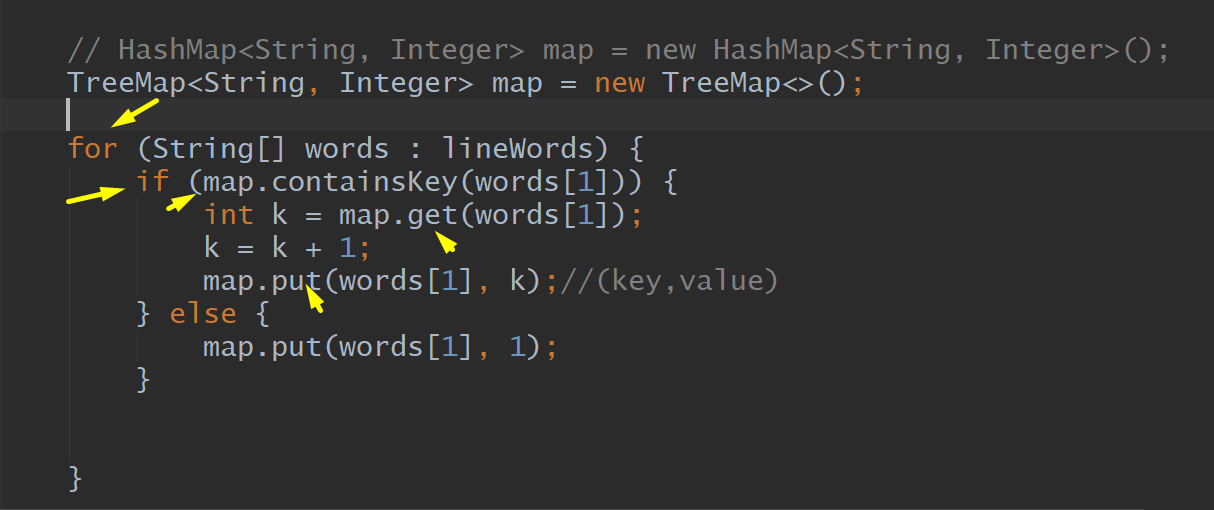
Map: key,value
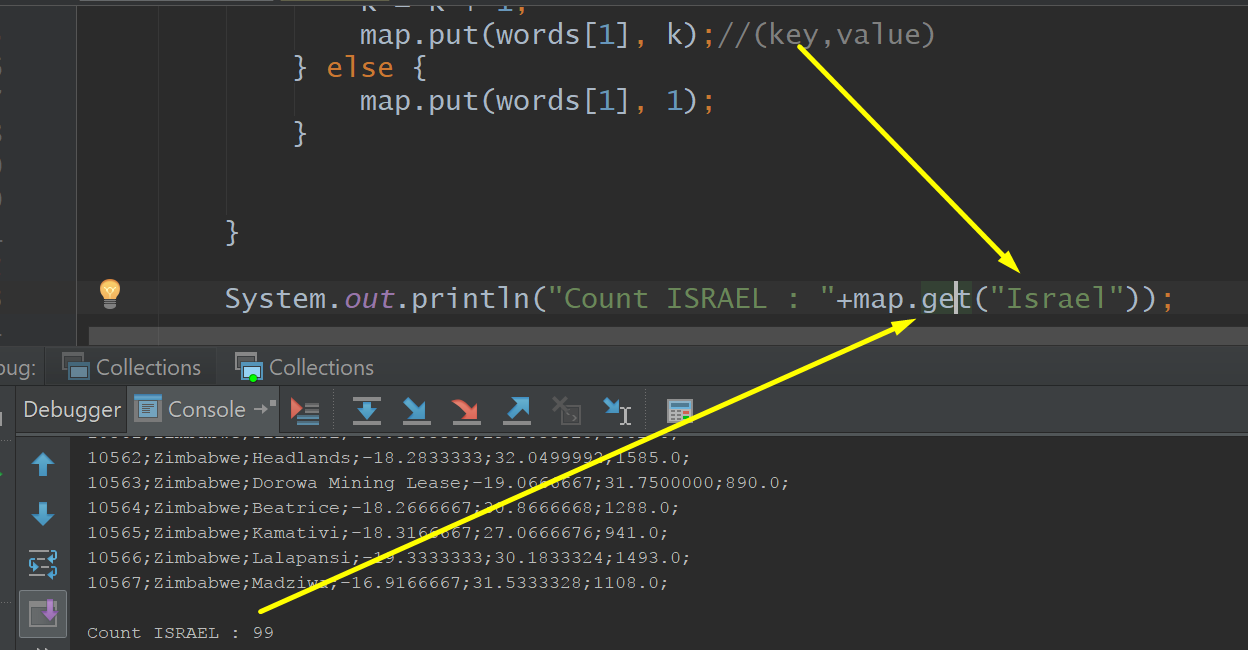
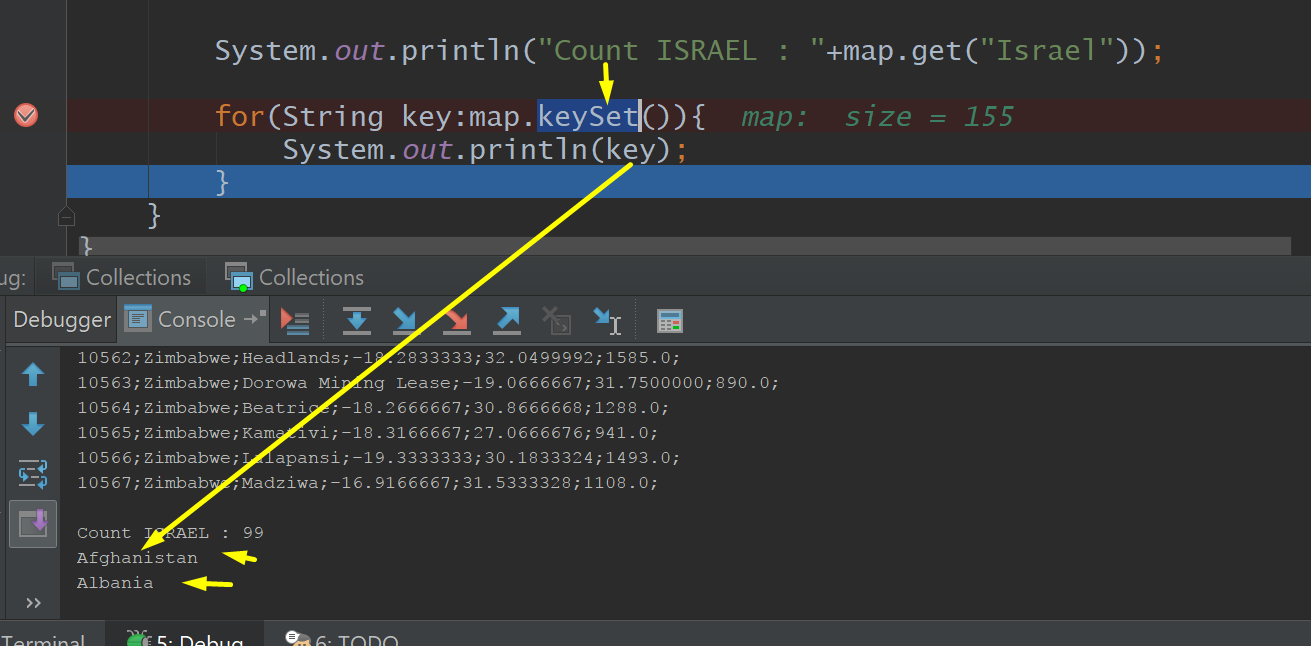
Get, KeySet
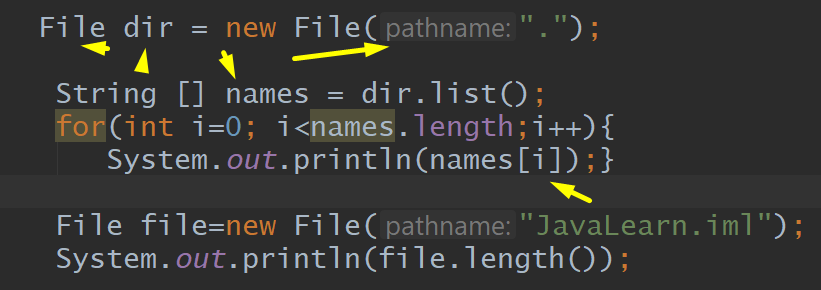
Dir.list, File, Dir, String, FileInputStream, FileNotFoundException, IOException
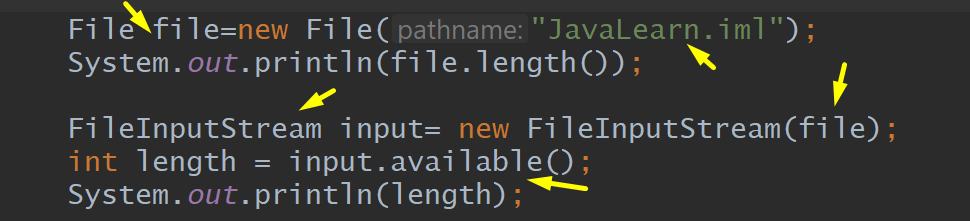
Read byte by Byte files, Array, Input.Read_File
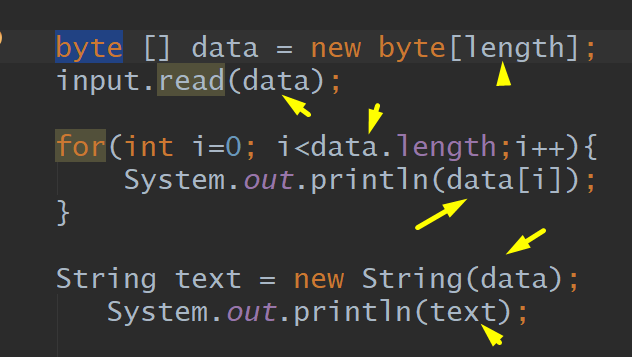
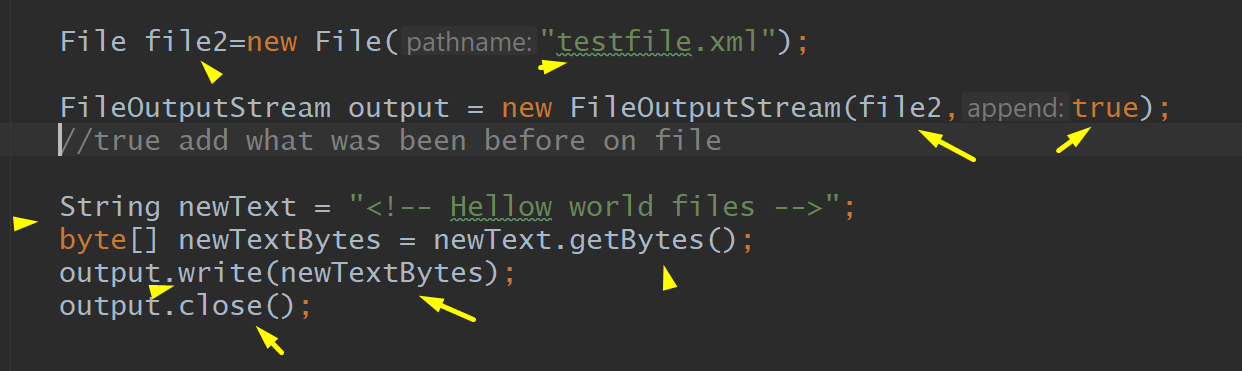
Add to file – no remove previous content
Output.write, String, File
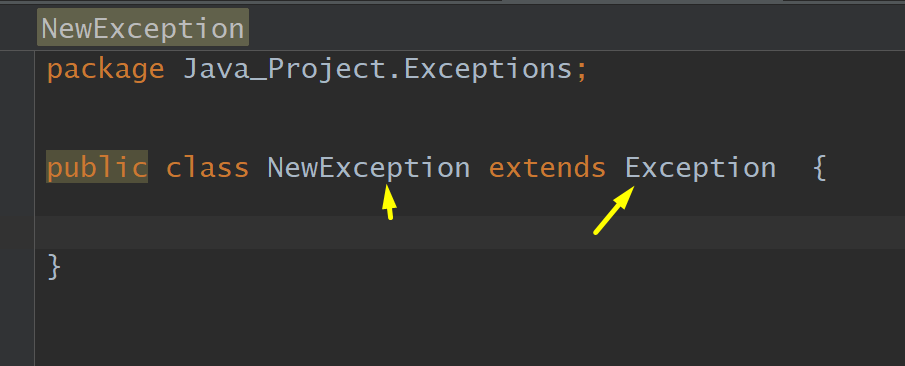
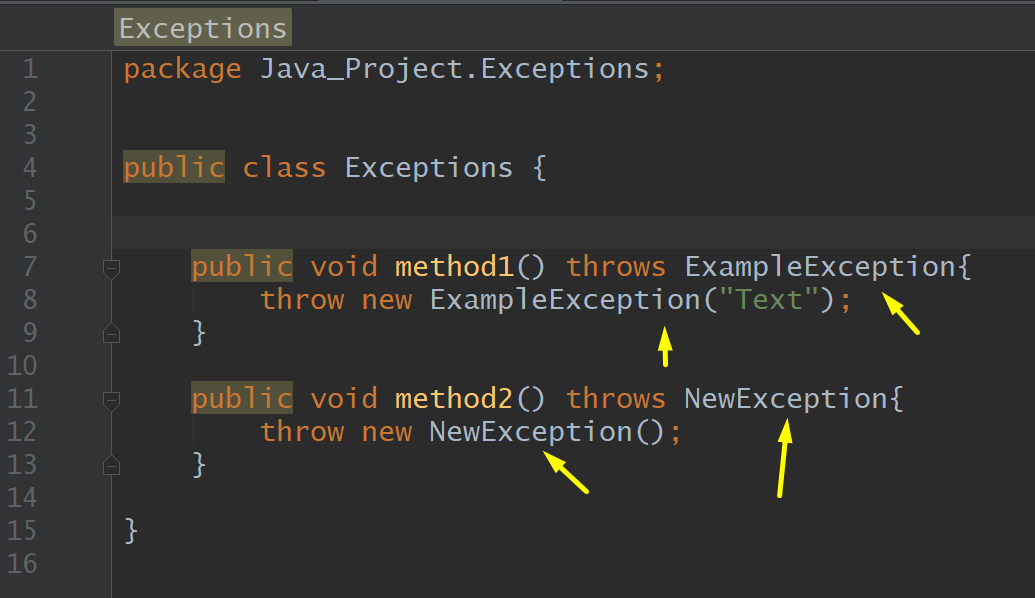
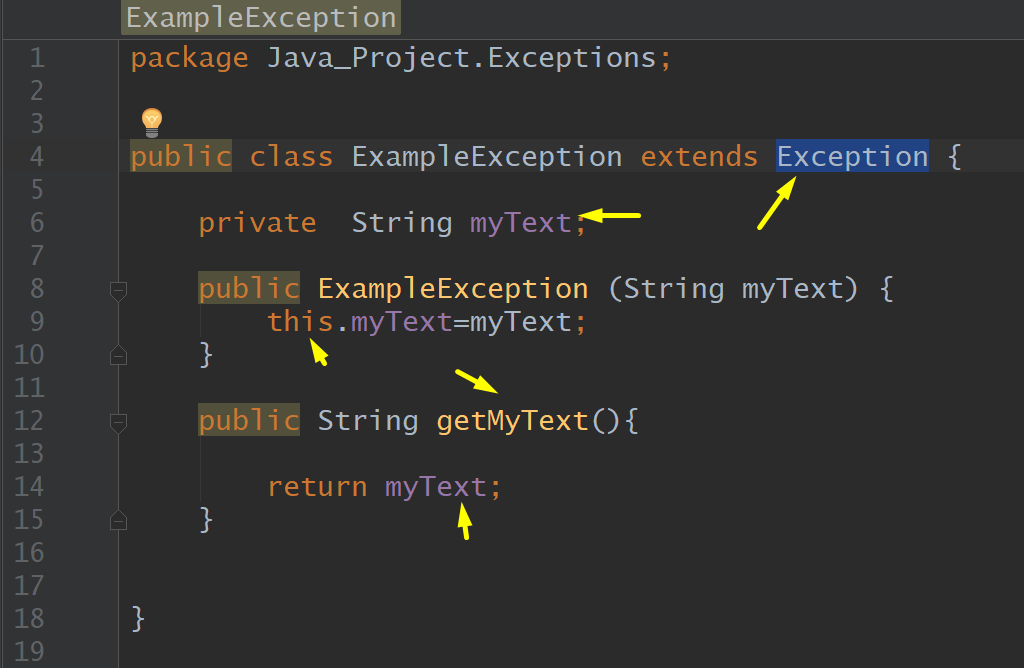
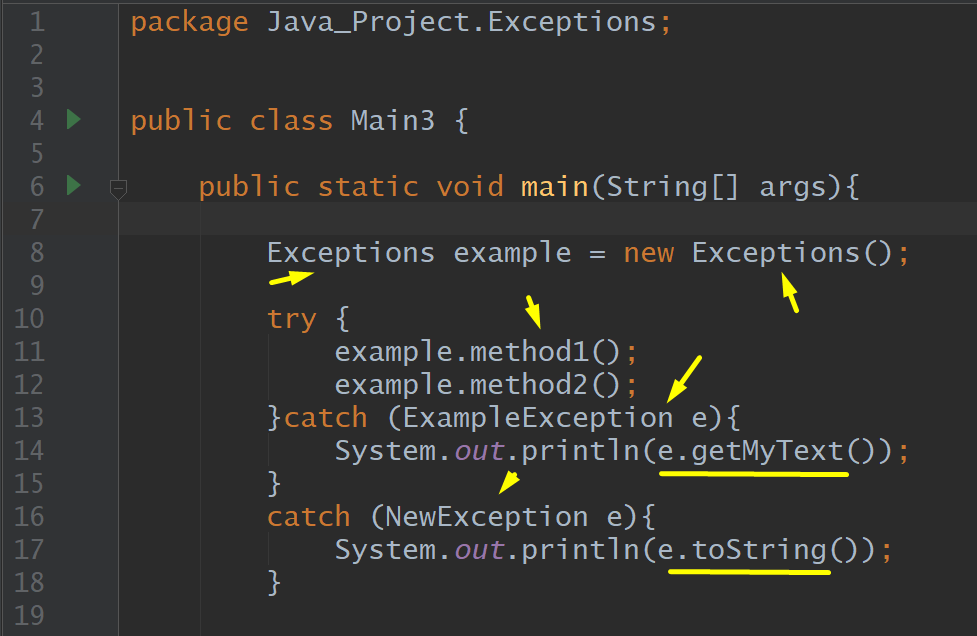
Exception, ExampleException, My Exception